badge_free
03/08 15:00
pre-registration required
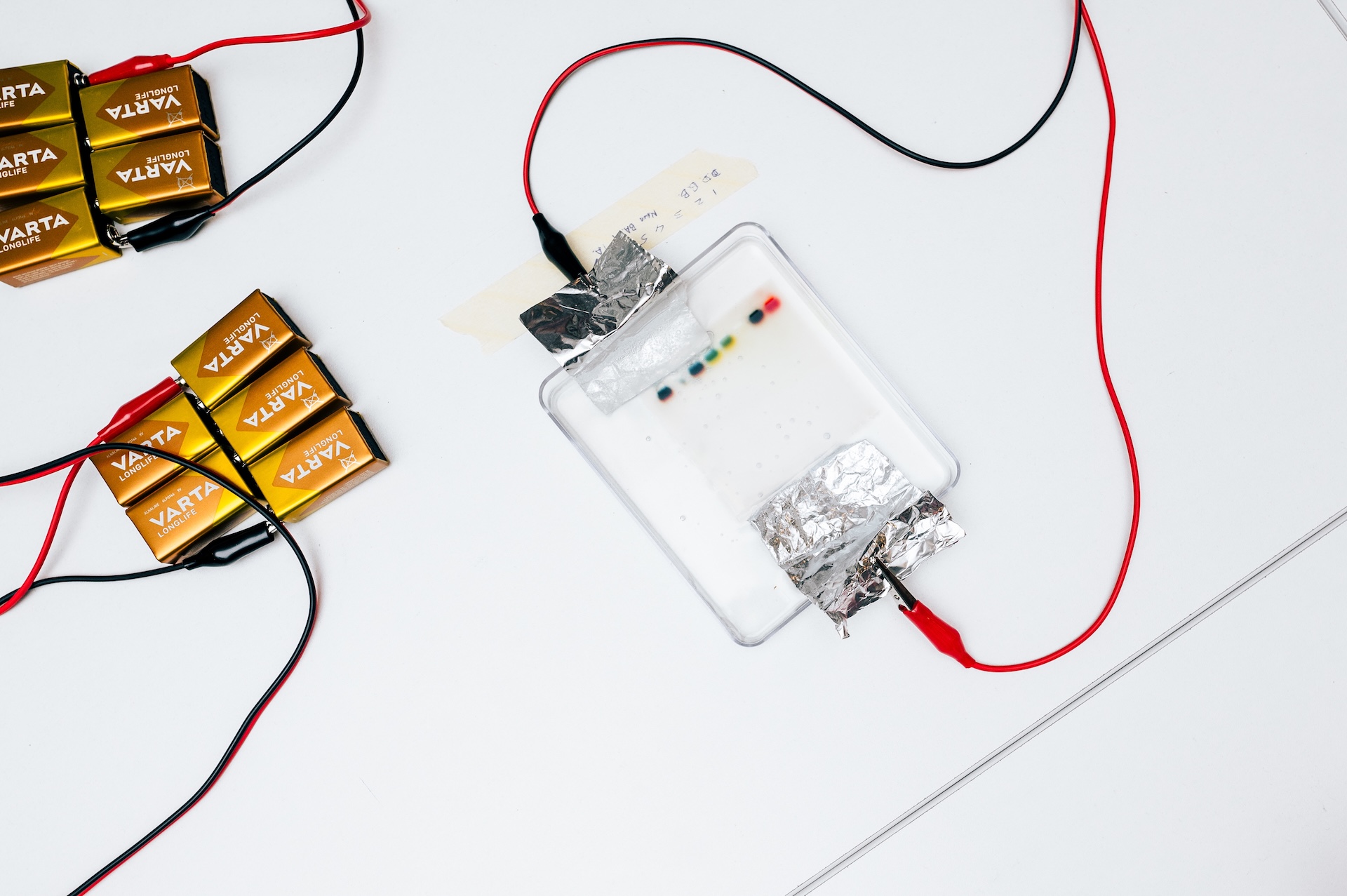
At this workshop, we will be conducting a gel electrophoresis experiment. During the workshop, participants will learn more about molecular biology and its applications, be able to create a setup for gel electrophoresis, and perform an analysis.
Gel electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method used in molecular biology to separate different molecules, such as DNA, RNA, or proteins, based on their size. This process is highly useful for studying genetic material, identifying individuals, analyzing PCR results, and detecting genetic diseases.

How does gel electrophoresis work?
Imagine a jelly, but with tiny holes. This "jelly" is called an agarose gel, and it acts as a filter. A mixture of molecules is introduced into the gel, and an electric field is applied. Since the molecules are charged, they start moving through the gel towards either the positive or negative pole: smaller molecules move faster, while larger ones move slower. As a result, the molecules are separated based on size and shape.
Where can it be applied?
- Identification of individuals: DNA analysis can accurately establish a person's identity.
- PCR analysis: After PCR (polymerase chain reaction), this method helps determine if a specific DNA is present in the sample.
- Detection of genetic diseases:** Genetic mutations that may cause diseases can be detected.
Gel electrophoresis is a fundamental tool in many laboratories, aiding researchers in understanding the genetic code, diagnosing diseases, and even solving criminal cases.